Introduction
There might be some cases that you need to have two or more processes connected. One solution which I guess is more common is using sockets on local
machine to connect process for interprocess communications. This is an example of interprocess communication using named pipes. The sample provides
a code snippet for C# and C++ process communications.
Background
Named pipes are mainly used for inter-process communications. It can be one way or duplex communication between a pipe server and one or more pipe clients.
Clients can have a stream which can be used to send/receive messages between processes. Name pipes has FIFO (First - In First - Out) behaviour.
Using the code
Two named pipes are created in this example. You have to run the C# application to initialise the pipes. Pipes are named myNamedPipe1
and myNamedPipe2, where in the C# application myNamedPipe1 is used for receiving and myNamedPipe2 for sending, and in C++ application
myNamedPipe1 is used for sending and myNamedPipe2 for receiving.
A class called NamedPipeServer is used in C# code to create instances of namedpipes. Servers should be started after creating an instance
of them and stopped when the application is closed. A Named pipe exists beyond the life of the process and must be deleted after the process is closed.
NamedPipeServer PServer1 = new NamedPipeServer(@"\\.\pipe\myNamedPipe1",0);
NamedPipeServer PServer2 = new NamedPipeServer(@"\\.\pipe\myNamedPipe2",1);
PServer1.Start();
PServer2.Start();
string Ms="Start";
do
{
Console.WriteLine("Enter the message");
Ms = Console.ReadLine();
PServer2.SendMessage(Ms, PServer2.clientse);
} while (Ms != "quit");
PServer1.StopServer();
PServer2.StopServer();
This snipped keeps sending messages until it gets quit command, then it closes both named pipes. Same name pipes with the exact same name are created in the C++ code and initialise.
LPTSTR lpszPipename1 = TEXT("\\\\.\\pipe\\myNamedPipe1");
LPTSTR lpszPipename2 = TEXT("\\\\.\\pipe\\myNamedPipe2");
Same as C# code, a thread processes received messages, and a loop in the main thread sends messages to the other application.
do
{
printf ("Enter your message: ");
scanf ("%s",buf);
if(strcmp (buf,"quit") == 0)
Write_St=FALSE;
else
{
WriteFile(hPipe1, buf, dwBytesToWrite, &cbWritten, NULL);
memset(buf,0xCC,100);
}
}while(Write_St);
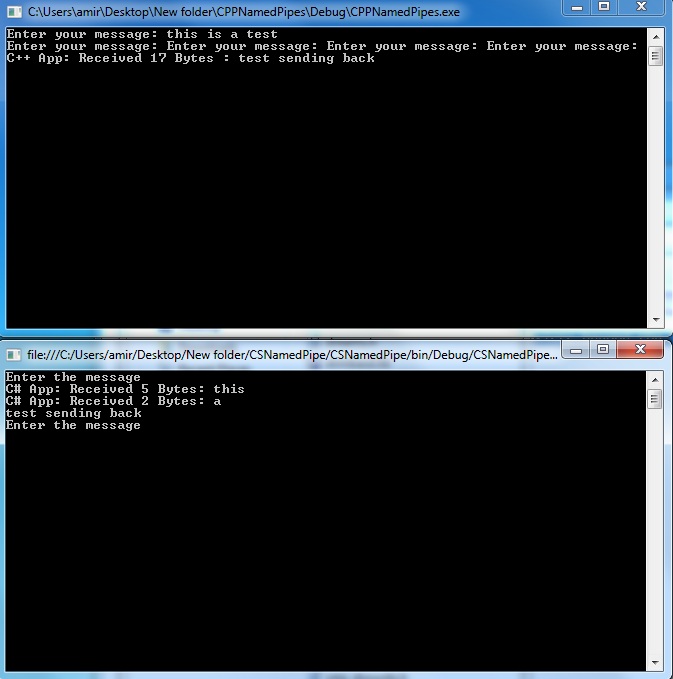
After running both applications you can send/receive messages between processes.